The mortality in sepsis remains very high, despite constant research and development activities by science and medical industry. The causes, in particular the malfunctions of the immune system, have not yet been able to be elucidated.
ARTCLINE would like to resolve this conflict with a new therapeutic approach.
The ARTICE® Therapy fights sepsis with immune cells from healthy donors.
The therapy uses Phagocytes, so-called granulocytes. The immune cells of the donor temporarily take over the disrupted function of the patient’s own immune cells. Inflammatory substances are removed from the patient’s plasma and, in addition, immunological messenger substances are also produced. They intended to support the regeneration of the patients’ immune system.
The extracorporeal immune cell-therapy replaces the immune cell-function and could be used as an additional therapy option in sepsis.
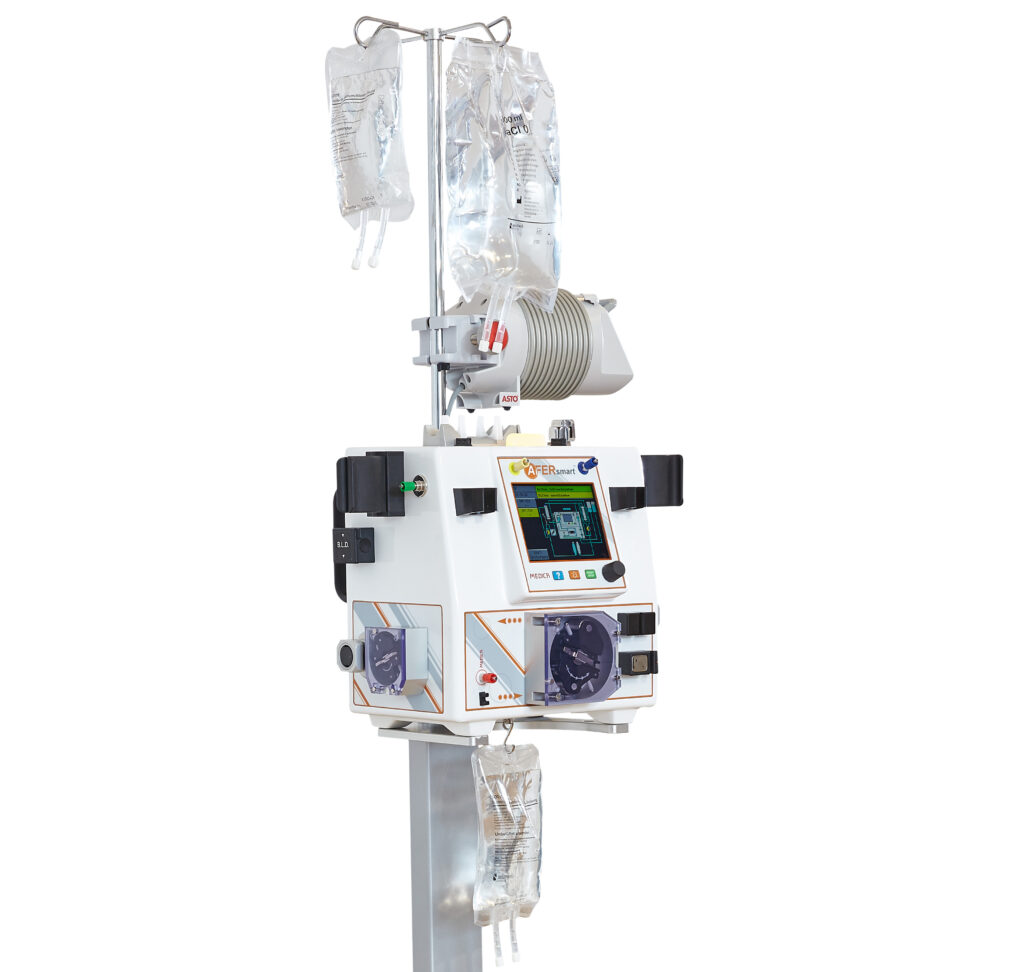
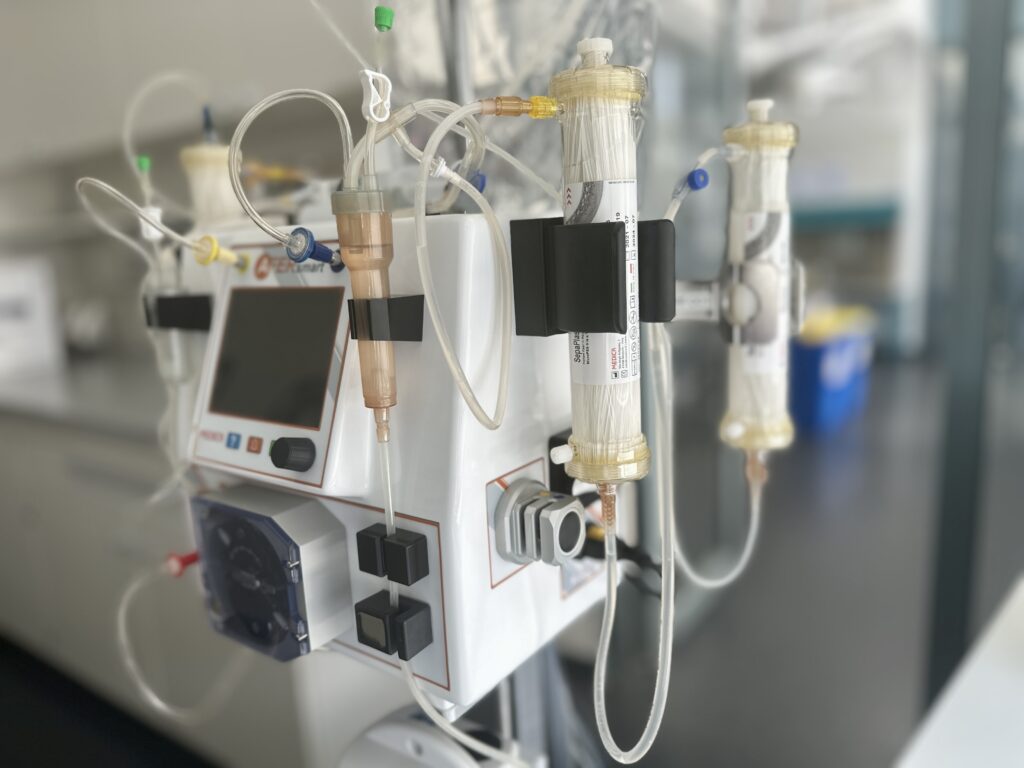
The technical implementation is similar to dialysis through an extracorporeal blood circulation, supplemented by plasmapheresis and a cell circulation.

In the extracorporeal blood circuit, the plasma is removed from the patient’s blood with the help of special plasma separators, e.g., separated by a plasma filter. The separated plasma is then transferred to a second circuit in which the immune cells of a healthy blood donor are located. This is where the patient’s plasma comes into direct contact with the donor immune cells. These bind and remove bacterial toxins as well as the patient’s own waste.
Furthermore, the healthy donor immune cells analyze the patient’s own immune messengers. The donor immune cells release various immune messengers, consequently to the signals received. Then, the treated plasma is separated from the donor immune cells by a second plasma filter and returned to the patient together with the patient’s blood. The immune messengers are supposed to reactivate the patient’s own immune system. Infections could be effectively treated, and organ malfunctions return to normal. The patient’s plasma is treated continuously for several hours.
The immune cells are obtained from healthy donors of the same blood group. The extraction takes place according to standard working instructions in a transfusion medical facility with GMP manufacturing license.
Both production and treatment procedures are patent protected in US and EU.